| MadSci Network: Engineering |
Calculating the wind load on a skyscraper is both really easy and
complicated. The basic formula for calculating the pressure of the wind
on any building is P = Ce * Cq * Qs * Iw. The factors come from tables
printed in the Universal Building Code, the most widely used building code
in the United States.
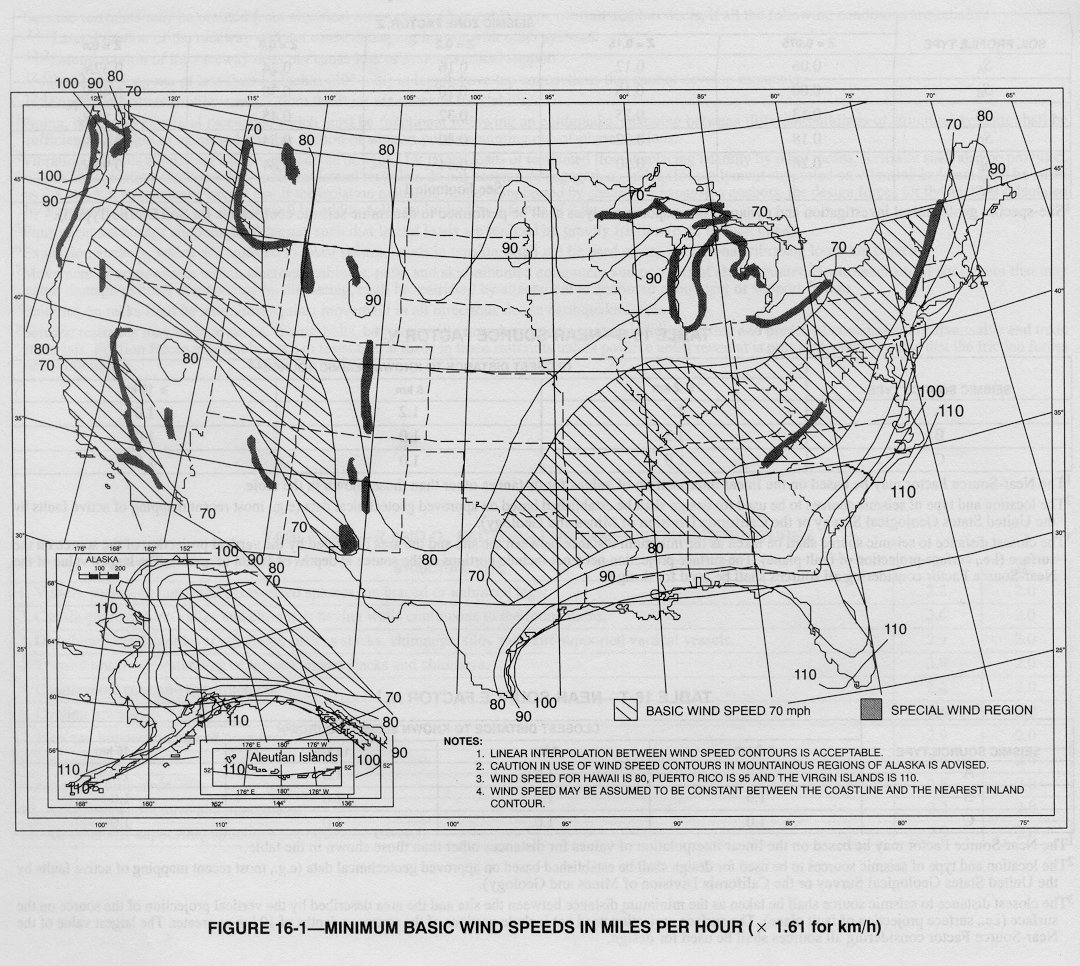
First, the design wind speed is taken from a map.
Iw is an occupancy factor, put into the formula to give important
buildings, such as hospitals, police and fire stations extra strength so
that they survive disasters other buildings do not. For an average
skyscraper, Iw = 1.0.
Ce is the Combined height, exposure and gust factor coefficient. It is
taken from this table:
Ht. ABOVE GND EXPOSURE. D EXPOSURE C EXPOSURE B
20 1.45 1.13 0.84
60 1.73 1.43 0.95
100 1.88 1.61 1.13
160 2.02 1.79 1.31
200 2.1 1.87 1.42
300 2.23 2.05 1.63
400 2.34 2.19 1.8
“Exposure B” is where there are buildings or trees covering 20% of the
ground for a mile around the site.
“Exposure C” it generally flat or open terrain
“Exposure D” is the most severe, where you would have flat , unobstructed
terrainon large bodies of water over one mile in extent, with winds at or
above 80 miles per hour possible.
The pressure applied by a steady wind, or Wind Stagnation Pressure, qs, is
given in this table:
BASIC WIND PRESSURE,
SPEED (MPH) (qs) PSF
70 12.6
80 16.4
90 20.8
100 25.6
110 31
120 36.9
130 43.3
The Pressure Coefficient, Cq, is given for different types of structure
and the way the wind strikes them. For a building over 40 feet but less
than 200 feet tall, the factor is 1.4, applied horizontally on the full
vertical projected area of the building’s walls, in any direction. So the
wind pressure would be multiplied by this factor times the area of the
building that the wind is hitting. That would be the width of a building
wall times the height if the wind comes square-on to the building. If the
wind is assumed to strike the building diagonally, the area is the width
from opposite corners times the height. An engineer will, of course, take
care to apply it in the direction that creates the greatest stress in her
structure.
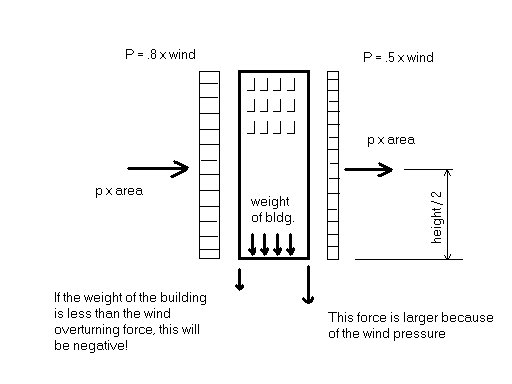
For buildings over 200 feet, a slightly different approach is taken,
called the Normal Force method. The wind is assumed to act
perpendicularly to a building’s walls, with a factor of 0.8 inward on the
windward side and 0.5 outward on the leeward side.
So, for a building say, 300 feet high and 100 feet wide, Exposure “D”,
winds of 80 miles per hour from the basic wind speed map, the design wind
load would be
P = 2.23 * 0.8 * 16.4 * 1.0 or about 29.3 pounds per square foot on the
windward side, and
2.23 * .5 * 16.4 *1 or about 18.3 psf on the downwind side. That’s
47.6 PSF on the building, times 100 feet wide by 300 feet tall, is
1,428,000 pounds trying to push the building over.
This is just a quick calculation. An engineer would divide the building
up into wind pressure zones based on the Ce factor and calculate the
pressure in each zone, resulting in a slightly different value of P.
Now I can see where you are thinking about what that pressure is going to
do to your building. It will try to push it over; This is called bending,
and it’s calculated by pretending that all that pressure is concentrated
at a point at the center of the area its acting on, then calculating how
far above ground that point is, and multiplying the pressure by that
distance. For our little exercise, it would be 1,428,000 pounds time ½
the height, or 150 feet. Now that is divided by one half the base width
of the building. This gives you what is called a Force Couple; the amount
of additional pressure that the downwind side has to carry because of the
wind, but more importantly the amount that the upwind side is reduced. If
the weight of the building and contents is not greater than this wind
uplift pressure, the building will need to be anchored down.
The other consideration is deflection, or how far the building will sway
sideways due to the wind. Usually, a value of 1/500th of the building’s
height is set as the allowable. Determining how much the wind will cause
your building to sway is a somewhat more complicated exercise, since you
have to calculate the stiffness of the structure. This can be done by
hand; but it requires considerable calculation, and some mathematical
concepts you will not be taught until your second year at a College of
Engineering.
Another thing I see that you have picked up on is that tall buildings sway
in high winds. (There were high winds in Chicago last week, and I could
hear our 30 story building creaking)Not only do tall buildings rock
against the force of the wind, but they sway from side ot side, cross-
wind. This requires a dynamic analysis, and is real difficult. Engineers
resort to computers in this case.
As for the wind tunnel, I encourage you to build one. It will be
difficult for you to achieve any precise results – research wind tunnels
cost millions. But you will learn about the techniques of wind tunnel
testing and model building for testing, which should be interesting and
fun. Try a big window fan and a long plywood or Masonite box.
By coincidence, the November issue of STRUCTURE magazine, a trade
publication put out by the National Council of Structural Engineer
Organizations, the Council of American Structural Engineers, and the
Structural Engineering Institute, has an article on high rise construction
and an article on wind tunnel testing. It is available on-line for awhile
at www.structuremag.org.
Good luck, and Build ‘Em High!
http://www.greatbuildings.com/cgi-
bin/gbi.cgi/John_Hancock_Center.html/cid_john_hancock_002.gbi
This is a link to Skyscrapers.com: http://www.emporis.info/en/


Try the links in the MadSci Library for more information on Engineering.