Date: Mon Nov 20 22:42:28 2000
Posted By: Michel Ouellet, Grad student in Microbiology / Immunology
Area of science: Cell Biology
ID: 974257346.Cb
Message:
Hi!
I don't know how much you know about mitosis so I will do a little review
first.
The cell cycle is divided into 5 steps, namely the G1, G0, S, G2 and M
phases. During the G1 phase, the cell prepares for the replication of its
DNA, the G0 phase occurs at the end of the G1 phase when a cell stops its
division for a while. If a mitotic signal is given, the cell exits G0 and
enters the S phase. It is during this phase that DNA replication occurs
and the amount of DNA of the cell doubles. After the S phase, the cell
enters the G2 phase in which the cell prepares for mitosis. All these
steps together are called the interphase. During the interphase, a
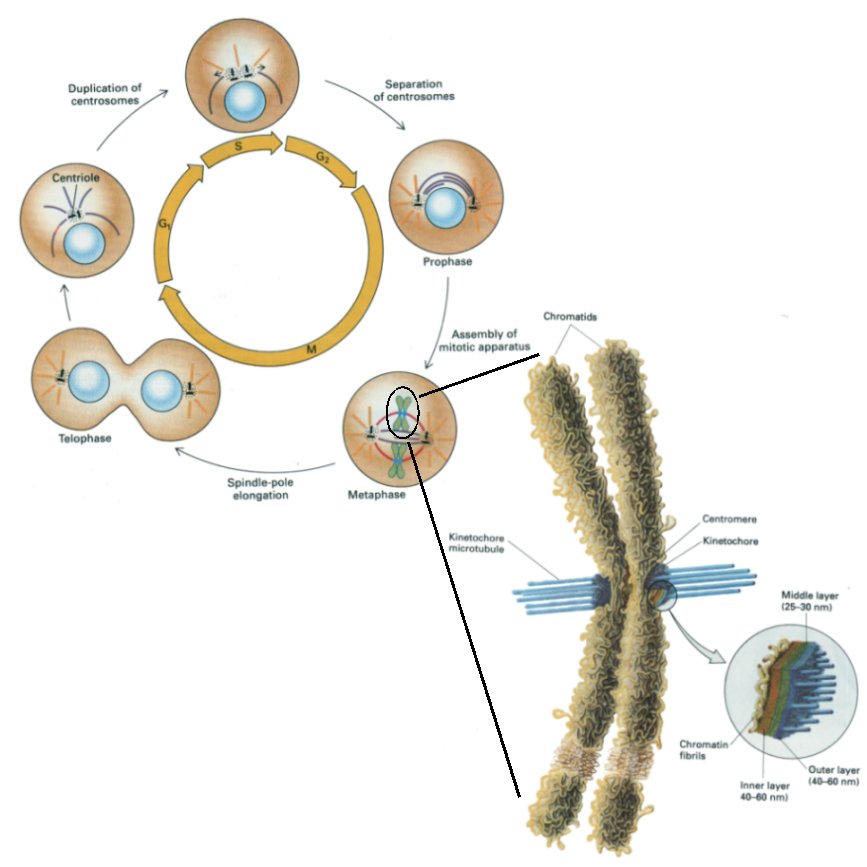
structure of the cell called the centrosome is duplicated and both
structures move along microtubules to each side of the cell.
When a cell enters mitosis, the nuclear membrane is disrupted and the
chromatin begins to condense into chromosomes. Each pair of chromosome is
linked at the centromere, a specialized region of the chromosome that is
situated at the constriction point giving the chromosome its characteristic
"X" shape. This region is responsible for the formation of a specific
protein assembly responsible for the movement of the chromosome called the
kinetochore (see figure).
At the beginning of the mitosis (prophase), the separated centrosomes begin
to extend kinetochore microtubules. These microtubules will specifically
"seek" any kinetochore-bearing chromosomes and allow the chromosome to move
along them. At this point (metaphase), chromosomes begin to congress (ie
to move toward the equator) using either motor proteins (like dynein or
kinesin) or using the highly dynamic properties of microtubules (which can
be built or destroyed very rapidly). It is not yet known specifically why
or how the chromosomes stay at the equator but it seems that each pair of
chromosome oscillates between each poles (centrosomes) indicating that
forces try to pull (or push) chromosomes from both sides.
 After a signal (increase in intracellular calcium concentration), each
sister chromatids will separate and move towards their respective poles
(anaphase). After chromosome separation is completed, the cell begins to
divide from its center and give rise to two new daughter cells (telophase).
The most characteristic event of the mitosis is the spindle formation which
is when the centromeres separate and the chromosomes congregate. Spindle
formation is the reason why chromosomes pair along the equator since it's
the middle point between two opposed centrosomes which try to move the pair
towards them.
I hope this answered your question as well as raised some more... if so,
don't hesitate to ask!
Ciao!
Mike.
After a signal (increase in intracellular calcium concentration), each
sister chromatids will separate and move towards their respective poles
(anaphase). After chromosome separation is completed, the cell begins to
divide from its center and give rise to two new daughter cells (telophase).
The most characteristic event of the mitosis is the spindle formation which
is when the centromeres separate and the chromosomes congregate. Spindle
formation is the reason why chromosomes pair along the equator since it's
the middle point between two opposed centrosomes which try to move the pair
towards them.
I hope this answered your question as well as raised some more... if so,
don't hesitate to ask!
Ciao!
Mike.
Current Queue |
Current Queue for Cell Biology |
Cell Biology archives
Try the links in the MadSci Library for more information on Cell Biology.
MadSci Home | Information |
Search |
Random Knowledge Generator |
MadSci Archives |
Mad Library | MAD Labs |
MAD FAQs |
Ask a ? |
Join Us! |
Help Support MadSci
MadSci Network,
webadmin@www.madsci.org
© 1995-2000. All rights reserved.
 After a signal (increase in intracellular calcium concentration), each
sister chromatids will separate and move towards their respective poles
(anaphase). After chromosome separation is completed, the cell begins to
divide from its center and give rise to two new daughter cells (telophase).
The most characteristic event of the mitosis is the spindle formation which
is when the centromeres separate and the chromosomes congregate. Spindle
formation is the reason why chromosomes pair along the equator since it's
the middle point between two opposed centrosomes which try to move the pair
towards them.
I hope this answered your question as well as raised some more... if so,
don't hesitate to ask!
Ciao!
Mike.
After a signal (increase in intracellular calcium concentration), each
sister chromatids will separate and move towards their respective poles
(anaphase). After chromosome separation is completed, the cell begins to
divide from its center and give rise to two new daughter cells (telophase).
The most characteristic event of the mitosis is the spindle formation which
is when the centromeres separate and the chromosomes congregate. Spindle
formation is the reason why chromosomes pair along the equator since it's
the middle point between two opposed centrosomes which try to move the pair
towards them.
I hope this answered your question as well as raised some more... if so,
don't hesitate to ask!
Ciao!
Mike.