Date: Thu Mar 8 10:03:22 2001
Posted By: Jeff Robertson, Faculty, Physical Sciences, Arkansas Tech University
Area of science: Earth Sciences
ID: 981852649.Es
Message:
In general, the earth recieves far more radiation from the sun at the
equator than at the poles averaged over the year. Therefore, hot air
should basically rise at the equators, move north or south, cool
and descend at the poles, returning back along the surface to the equator.
Because the earth rotates, a single cell of circulation cannot exist
in each hemisphere and there are actually three circulation cells
in each hemisphere (North and South for six total). See figure 1.
Figure 1
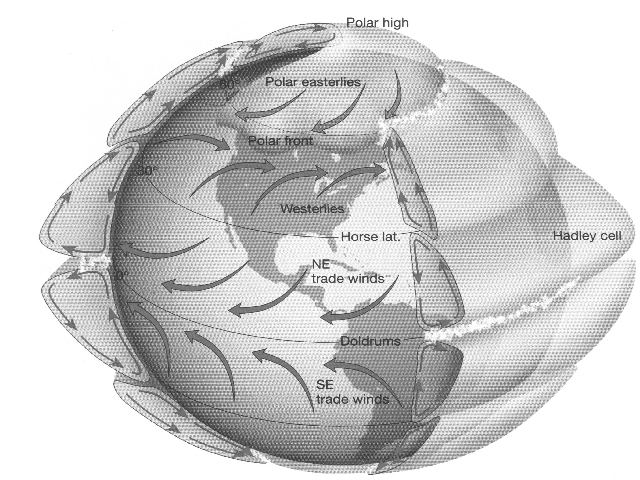 Rising air leads to low pressure near the surface and sinking
air leads to high pressure near the surface. This leads to semi-permanent
pressure zones on the earth because of these three circulation
cells. See figure 2.
Figure 2
Rising air leads to low pressure near the surface and sinking
air leads to high pressure near the surface. This leads to semi-permanent
pressure zones on the earth because of these three circulation
cells. See figure 2.
Figure 2
 In addition, as air travels along, it experiences the coriolis force
because of earth's rotation.
This force tends to deflect motion the the right in the northern
hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. The combination
of the three (six) major circulation cells, the semi-permanent
pressure zones and the coriolis force
cause the generalized circulation patterns seen in the figures.
(i.e. "Easterlies" and "Westerlies")
In addition, as air travels along, it experiences the coriolis force
because of earth's rotation.
This force tends to deflect motion the the right in the northern
hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. The combination
of the three (six) major circulation cells, the semi-permanent
pressure zones and the coriolis force
cause the generalized circulation patterns seen in the figures.
(i.e. "Easterlies" and "Westerlies")
Current Queue |
Current Queue for Earth Sciences |
Earth Sciences archives
Try the links in the MadSci Library for more information on Earth Sciences.
MadSci Home | Information |
Search |
Random Knowledge Generator |
MadSci Archives |
Mad Library | MAD Labs |
MAD FAQs |
Ask a ? |
Join Us! |
Help Support MadSci
MadSci Network,
webadmin@www.madsci.org
© 1995-2001. All rights reserved.
 Rising air leads to low pressure near the surface and sinking
air leads to high pressure near the surface. This leads to semi-permanent
pressure zones on the earth because of these three circulation
cells. See figure 2.
Figure 2
Rising air leads to low pressure near the surface and sinking
air leads to high pressure near the surface. This leads to semi-permanent
pressure zones on the earth because of these three circulation
cells. See figure 2.
Figure 2
 In addition, as air travels along, it experiences the coriolis force
because of earth's rotation.
This force tends to deflect motion the the right in the northern
hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. The combination
of the three (six) major circulation cells, the semi-permanent
pressure zones and the coriolis force
cause the generalized circulation patterns seen in the figures.
(i.e. "Easterlies" and "Westerlies")
In addition, as air travels along, it experiences the coriolis force
because of earth's rotation.
This force tends to deflect motion the the right in the northern
hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. The combination
of the three (six) major circulation cells, the semi-permanent
pressure zones and the coriolis force
cause the generalized circulation patterns seen in the figures.
(i.e. "Easterlies" and "Westerlies")